,
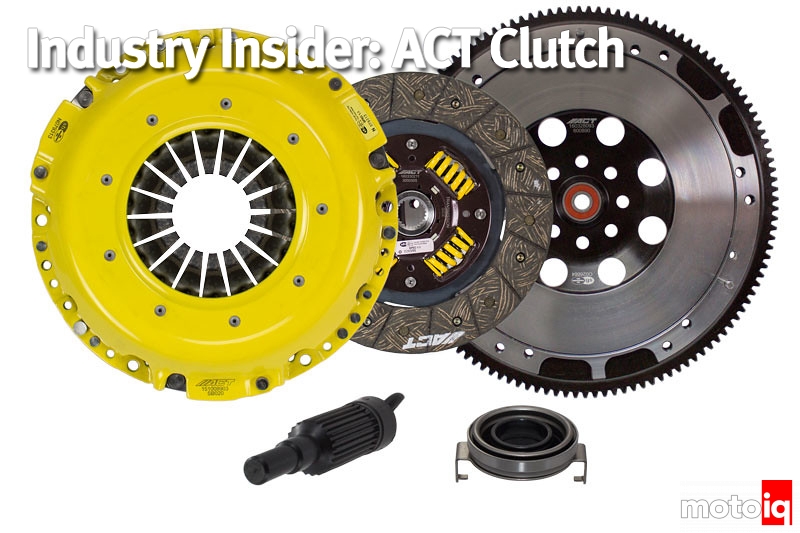
 The disc is held together by these large headed rivets which also serve as the stops for the sprung hub. The headed rivets spread out the load encountered by acting as a bump stop and holding the disc together.
The disc is held together by these large headed rivets which also serve as the stops for the sprung hub. The headed rivets spread out the load encountered by acting as a bump stop and holding the disc together.  This is the disc marcel spring. The marcel spring in the case of the ACT disc couples the friction material to the hub. It also acts like a wave spring under the friction material that allows it to give. This give increases the engagement travel and makes the engagement smoother. This makes the clutch easier to drive, especially from a standing start. To strengthen the disc, the marcel is 20% thicker than the stock part.
This is the disc marcel spring. The marcel spring in the case of the ACT disc couples the friction material to the hub. It also acts like a wave spring under the friction material that allows it to give. This give increases the engagement travel and makes the engagement smoother. This makes the clutch easier to drive, especially from a standing start. To strengthen the disc, the marcel is 20% thicker than the stock part.  The disc's friction material is bonded and riveted to a steel backing. This improves the friction materials burst strength and helps conduct heat away from the friction surface.
The disc's friction material is bonded and riveted to a steel backing. This improves the friction materials burst strength and helps conduct heat away from the friction surface. The friction material is an organic compound that has smooth and streetable friction characteristics yet has a stable coefficient of friction at higher heat levels due to it's high copper content. It also has improved wear characteristics over stock.
 This is how the disc assembly stacks up before riveting the upper friction and steel in place.
This is how the disc assembly stacks up before riveting the upper friction and steel in place.  The fully assembled disc riveted together.
The fully assembled disc riveted together.  Each assembled pressure plate is QC tested for proper clamping force, engagement and disengagement characteristics.
Each assembled pressure plate is QC tested for proper clamping force, engagement and disengagement characteristics.  The bottom green trace is engagement and disengagement forces for the stock pressure plate. The red trace is the ACT pressure plate. You can see how the ACT pressure plate has greater clamping force. The ACT pressure plate has 2900 lbs of clamping force vs 1900 lbs for the stock part.
The bottom green trace is engagement and disengagement forces for the stock pressure plate. The red trace is the ACT pressure plate. You can see how the ACT pressure plate has greater clamping force. The ACT pressure plate has 2900 lbs of clamping force vs 1900 lbs for the stock part.